The Solar Power Inverter
One of the key components of a residential solar energy system is the solar power inverter.
Home solar power systems can be used to provide power for many standard electrical devices and household appliances. But in order to provide this power, these systems require solar inverters.
What is a Solar Inverter
For more information about the basics of electricity, take a look at our page on...
The purpose of an inverter is to change Direct Current (DC) electricity into Alternating Current (AC) electricity. It also will increase the voltage of the AC electricity to 120 Volts AC (if you're in the United States) or 240 Volts AC (if you're in most other parts of the world).
But why is a solar power inverter needed in the first place?
Well, a solar inverter is needed because the electricity generated by your solar panels is DC electricity. In order to use the generated solar power with your electrical devices and household appliances, it needs to be converted to the standard voltage AC electricity for your region.
Types of Solar Inverters
Solar inverters can be categorized by the type of solar power system they are used with...
- Grid Tie Inverter
- Off Grid Inverter
- On/Off Grid Inverter
A Grid Tie Inverter is used with a grid-tied PV system. This type of solar power inverter takes the DC electricity generated by the solar panels and converts it to AC electricity directly. It channels the AC electricity to your home's breaker panel where it is either used by your household loads or, if you are signed up for net-metering, sends it to the utility grid.
An Off Grid Inverter is used with a stand-alone or off-grid solar system. An off-grid solar system typically uses batteries to store the DC electricity generated by your solar panels. The inverter converts the DC electricity from the batteries into AC electricity for use in your home.
An On/Off Grid Inverter is used with a grid-tied PV system with battery backup. This type of inverter allows you to connect your home to the utility grid and use power from a battery bank. Unlike a pure grid tie inverter, this type of inverter is able to continue transferring power to your home when the utility has a blackout. During a blackout, a grid tie inverter will not be operational.
Solar Power Inverter Considerations
Three factors homeowners should consider when evaluating inverters are...
- Power Quality
- Power Rating
- Efficiency
Power Quality
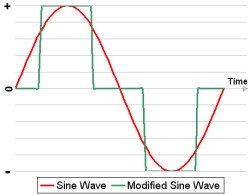
The quality of the AC electricity generated by your inverter is important for household use. For most home solar power systems, you will want to use what's known as a pure sine wave inverter. This is also known as a true sine wave inverter.
This is considered "clean" power and is suitable for all household electrical applications such as computers, televisions, and microwaves. It is the same type of power provided by the utility companies.
Some solar power inverters generate "dirty" power. This type of inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity that is in the form of a stepped square wave and is known as a modified sine wave inverter.
The AC electricity generated by this type of inverter can have a noticeable impact on your electrical equipment's performance. For example, audio speakers will buzz, microwaves will take longer to heat food, and television and computer monitors will display rolling lines.
Power Rating
The amount of power the inverter can handle is known as it's power rating. Two critical power ratings you will need to understand for your inverter are it's continuous rating and it's surge rating.
An inverter's capacity refers to it's continuous rating. This is the amount of power it can supply continuously. So when you see a 4000 W inverter, this is referring to it's continuous rating. The inverter you choose should have a continuous rating that is about 25% higher than the maximum power you will need to deliver to your household loads.
Household loads such as refrigerators and washing machines may require a short-term boost in power to get started. The amount of power can be 2 to 3 times the normal operating power, so make sure to check that your inverter's surge rating can handle that amount of power for a few seconds.
Efficiency
Inverter efficiency is another factor to consider. An inverter's efficiency indicates how much of the input DC power it converts into AC power. This will never be 100% because the inverter uses some of the input DC power itself, generally around 10-25 W.
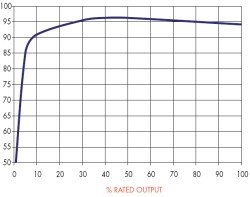
The efficiency of an inverter depends on the power output level it is operating at. At different power levels, it will be operating at different efficiencies .
Inverters operate at maximum efficiency at a power level know as it's peak efficiency point. This is generally at around 20-30 percent of it's maximum power rating. So if you have a 4000 W inverter, it's peak efficiency point will be between 800 and 1200 W.
An inverter's efficiency is shown in an efficiency curve. What you will see is that the inverter's efficiency will increase sharply until it reaches it's peak efficiency point. It will then remain close to level, decreasing slightly as it approaches it's rated power output.
Don't stay focused on peak efficiency. It's important, but you also have to consider the whole efficiency curve. Ideally, your electricity use should be at or above your inverter's peak efficiency point. By choosing a solar power inverter that matches your electricity use, you will be able to better utilize the solar electricity you generate.
Home > Solar Power Inverter



